Breast feeding provides infants with the best nutrition and start in life1, helping them develop a healthy gut microbiome, a strong immune system and optimal brain development. But for some mothers and infants, breastfeeding is not an option.
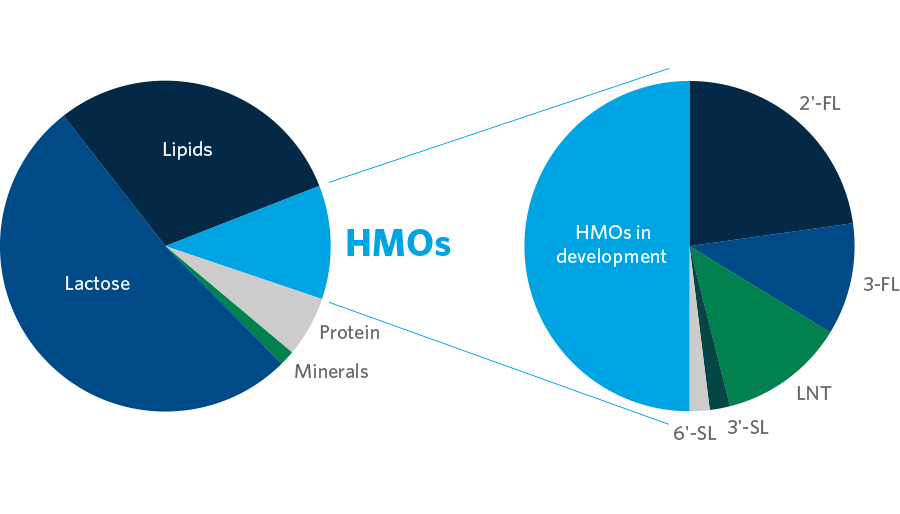
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are carbohydrates, or complex milk sugars, that are only found in human milk. In fact, HMOs are the third most abundant solid component of human milk, outnumbered only by lipids and lactose.
Scientific data indicates that each HMO may bring a unique health benefit, so each has its own structure and function – its own purpose. There are more than 150 HMOs known so far to occur in human milk. At Chr. Hansen we are today producing the five most dominant HMOs and are developing new HMOs for commercialization. These are all supported by scientific studies.
Recent scientific research shows health benefits of HMOs on:
- Shaping a healthy infant gut microbiome through increasing the abundance of good gut bacteria2
- May support brain development3
- Supporting the maintenance of a well-balanced immune system4
- Reducing the risk of bacterial imbalance through promoting a healthy gut microbiome5
- Maturing and maintaining the integrity of the intestine6.
Supplemented at the same level as the level in breast milk HMOs may therefore play a role in the growth and development of infants, including cognitive development.
MyOli is a trademark of Chr. Hansen A/S.
References
Open
Close
1 “The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends breastfeeding exclusively for the first six months, followed by continued breastfeeding together with complementary foods.“ World Health Organization. International Code of Marketing of Breast-Milk Substitutes. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9241541601 Accessed June 13, 2023.
2 Gotho et al., 2018, Kostopoulus et al., 2020.
3 Berger et al., 2020.
4 Göhring et al., 2016, Ayechu-Muruzabal et al., 2018.
5 Asadpoor et al., 2020.
6 Oliveros et al., 2021.